Fabric Expansion Joints and
Factors Influencing their Design
Fabric expansion joints perform a function of compensating for duct misalignment and duct thermal growth typical in power plants and other ducting systems. Proper design of these joints starts with asking the right questions about the application, providing the correct answers, and applying design rules to arrive at the appropriate solution.
The guiding principle for fabric joint design is to protect the fabric belt element so that it can absorb movement while retaining the media. The longevity of the belt life can be diminished by many factors. These factors include excessive temperature, harsh corrosives, exposure to abrasive particulate, excessive movements, fly ash weight against the belt, and high internal pressures. All of these problems can be solved if they are anticipated. The quality of the expansion joint design is only as good as the information provided up front. A realistic and accurate analysis of the system is step one. Assuming that is taken care of, these guidelines are a brief introduction to factors that influences the success of the expansion joint.
Temperature
Fabric gas seal membranes have specific temperature capabilities. When necessary, the addition of insulating materials between the temperature source and the belt will extend the service life. The magnitude of the temperature will determine the thickness of the integral belt insulation and if a separate high density insulation pillow is required.
The belt attachment flanges should be outboard of the cavity and have sufficient standoff from the duct. Care should be taken to avoid external insulation or lagging outside of the belt which prevents proper heat dissipation.
Chemical Attack
Applications that do not have high temperatures sometimes have a different problem. Relatively low temperatures in flue gas ducting can lead to corrosive condensation. In these situations, a chemical barrier is required to protect the load bearing fiberglass carcass of the belt. External insulation over the joint in these locations can reduce condensation and heat loss.
Movements
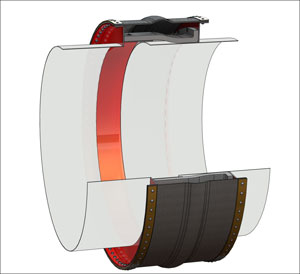 Generally, movements occur along the axis of the duct (usually compression but occasionally extension) or at right angles (lateral). The key to being able to handle these movements is having the proper width of belt installed in a sufficient span. For compression, a ratio of installed belt span to movement roughly at 4:1 is suggested. The lateral capability is influenced by the amount of belt slack available. Concurrent axial compression will provide the slack thus allowing more lateral. In certain situations, there is lateral offset in the cold installed condition. This may require "pre-compression" of the joint which is in essence just providing extra belt width. Generally, movements occur along the axis of the duct (usually compression but occasionally extension) or at right angles (lateral). The key to being able to handle these movements is having the proper width of belt installed in a sufficient span. For compression, a ratio of installed belt span to movement roughly at 4:1 is suggested. The lateral capability is influenced by the amount of belt slack available. Concurrent axial compression will provide the slack thus allowing more lateral. In certain situations, there is lateral offset in the cold installed condition. This may require "pre-compression" of the joint which is in essence just providing extra belt width.
Abrasion
In flue gas ducting with particulate, a liner should be used to protect the belt from direct exposure. If the pressure is negative, the belt stand-off from the gas stream should be increased to keep the belt from being pulled into the gas stream or against the liner. Belt clamping bar edges next to the fabric should be radiused. The belt attachment flange should also be smooth and free of rough surfaces.
Pressure Fluctuations
Fabric expansion joints exposed to sudden pressure fluctuations, such as near ID fans and dampers, may result in the belt "fluttering". The fabric will fatigue over time resulting in tears. Using stiffer fabric material, installing a liner and increasing the standoff are steps to take to avoid flutter.
Summation
Each location throughout a ducting system can have different conditions that affect the design of expansion joints. As a result, there isn't one design that can fit all applications. The goal of the expansion joint supplier is to work with engineers and end users to provide the optimum economical solutions.
|